Sony Shows RGB LED Technology for TVs – It’s Designed to Replace Mini-LED and OLED
Its main feature is the absence of light filters that reduce the brightness and saturation of the picture. Instead, backlight LEDs are responsible for the formation of color on the screen. I will tell you about RGB LED and its device in more detail.

What is RGB LED
One of the first TVs with new generation screens was shown by Sony as a non-serial demonstration sample. RGB LED panels are most similar to mini-LEDs in their design: they have a backlight and liquid crystal pixels that regulate the brightness and intensity of the light passing through them. But instead of white or blue diodes, whose light is colored in the desired shades using special filters, RGB LED uses colored subpixels at once: red, green and blue - hence the name.
The rejection of the light filter allowed to increase the saturation and brightness of the image. According to a Sony representative, the brightness of such panels will reach 4000 cd/m² — up to two times more than the most advanced models of 2024. In addition, it is planned to improve the quality of shade transmission and the smoothness of transitions between them, as well as viewing angles. At the same time, the technology will make the production of large diagonals easier and cheaper.
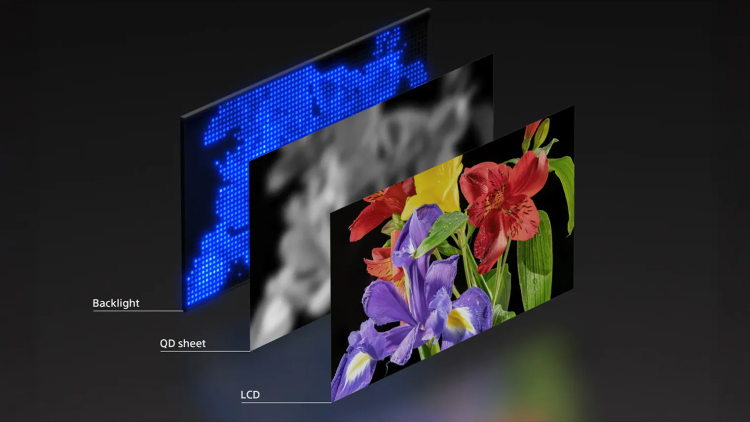
When will RGB LED TVs go on sale?
At the presentation, Sony hinted that it is developing new technology not only for the professional segment, but also for consumer TVs. At the same time, mass production of such panels should begin in 2025, and the first models could hit the market in 2026 or 2027.
Similar solutions have previously been announced by other companies such as Samsung Display and Hisense. Everyone calls this technology slightly differently, but for convenience you can use the abbreviation RGB LED.
How modern screens differ from each other and from RGB LED
Televisions and monitors use different technologies that vary greatly in complexity, image quality, and production cost. There are four main levels:
- The most basic LCD panels like LED and DLED offer low brightness in the 200-400 nit range and poor contrast, with "whitish" blacks.
- Mid-range models most often belong to the QLED family with high brightness, from 350 to 1500 nits, and good color rendering. They also have problems with the depth of black: dark areas of the image are “blue”.
- The most expensive and advanced screens now are OLED and mini-LED. They produce rich and clear colors, provide good contrast and reach brightness in HDR up to 2000 nits or higher. Mini-LED is bright, but the black color is not perfect. OLED transmits a more saturated picture, but sometimes it can seem too bright.
- At a higher level is micro-LED technology - various companies have been trying to bring it to the mass market for many years, but due to the high cost, such panels with maximum brightness, contrast and reliability are currently used only for commercial purposes.
RGB LED screens can take their place in the premium segment. They combine the brightness and color saturation of mini-LEDs with the high contrast inherent in OLEDs. In theory, they are not afraid of burnout, and such panels can be made huge - with a diagonal of more than 100 inches, while the maximum size of OLEDs for most manufacturers is limited to 88 inches.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0





![Transfer/ Postings Senior Superintendent Police Hyderabad [Notifications]](https://pakweb.pro/uploads/images/202402/image_100x75_65d7bb0f85d5f.jpg)
![Amazing Text Animation Effect In CSS - [CODE]](https://pakweb.pro/uploads/images/202402/image_100x75_65d79dabc193a.jpg)